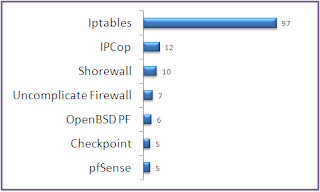
Top 5 Open Source Firewall
User, which allows a system administrator to configure the tables provided by the firewall of the Linux kernel (as units executed Netfilter different) rules and chains and stores. And is currently using the kernel modules and different programs for different protocols; iptables applies to IPv4, ip6tables to IPv6, arp tables for the rehabilitation of agriculture, as a special ebtables Ethernet frames
IPtables require elevated privileges to work must be carried out by the root user, but it failed to function. In most Linux systems, iptables is installed as /usr/directory/iptables and documented in the man page to him [2], which can be opened using `man iptables` when installed. Can also be found in the /sbin/iptables, but since iptables is not "dual core", but more like a service, is still the preferred place / usr / Guide
The (old) information from http://www.ipcop.org can be found here: http://www.ipcop.org/index-pn.php Be aware that most of the information is old and obsolete.
One day there may be a flashy, web-2.0 style homepage, but until then the page you are now reading is the home of IPCop.
Shorewall is a gateway/firewall configuration tool for GNU/Linux.
For a high level description of Shorewall, see the Introduction to Shorewall.
1) IPTable
User, which allows a system administrator to configure the tables provided by the firewall of the Linux kernel (as units executed Netfilter different) rules and chains and stores. And is currently using the kernel modules and different programs for different protocols; iptables applies to IPv4, ip6tables to IPv6, arp tables for the rehabilitation of agriculture, as a special ebtables Ethernet frames
IPtables require elevated privileges to work must be carried out by the root user, but it failed to function. In most Linux systems, iptables is installed as /usr/directory/iptables and documented in the man page to him [2], which can be opened using `man iptables` when installed. Can also be found in the /sbin/iptables, but since iptables is not "dual core", but more like a service, is still the preferred place / usr / Guide
2) IPCop
The IPCop Firewall is a Linux firewall distribution. It is geared towards home and SOHO users. The IPCop web-interface is very user-friendly and makes usage easy.The (old) information from http://www.ipcop.org can be found here: http://www.ipcop.org/index-pn.php Be aware that most of the information is old and obsolete.
One day there may be a flashy, web-2.0 style homepage, but until then the page you are now reading is the home of IPCop.
3) ShoreWall
Shorewall is a gateway/firewall configuration tool for GNU/Linux.
For a high level description of Shorewall, see the Introduction to Shorewall.
- Uses Netfilter's connection tracking facilities for stateful packet filtering.
- Can be used in a wide range of router/firewall/gateway applications.
Supports centralized firewall administration.
QuickStart Guides (HOWTOs)
Extensive documentation is available in both Docbook XML and HTML formats.
Flexible address management/routing support (and you can use all types in the same firewall):
Blacklisting of individual IP addresses and subnetworks is supported.
VPN Support.
Support for Traffic Control/Shaping.
Media Access Control (MAC) Address Verification.
Traffic Accounting.
Bridge/Firewall support
IPv6 Support
Works with a wide range of Virtualization Solutions
Additional Firewall Software
Following are additional firewalls mentioned by readers along with the total number of votes it received.- CheckPoint FireWall-1 5
- pfsense 5
- Firestarter 5
- Netfilter 4
- SmoothWall Express 3
- Guarddog 3
- ipchain 3
- Endian 2
- Susefirewall 1
- Cisco ASA/PIX 1
- ClearOS 1
- APF 1
- Firewall Builder 1
- Auto firewall in Puppy Linux 1
- Drawbridge 1
- Monowall 1
- Firehol 1
- SuSEfirewall2 1
- Plesk 1


Comments
Post a Comment